Key Takeaways
The rise of cloud computing and SaaS has revolutionized software delivery, driving a shift to subscription-based models that have reshaped industries, consumer behavior, business processes, and organizational structures.
- SaaS has disrupted various sectors, including entertainment and accounting, leading to changes in consumer behavior and expectations.
- SaaS companies require flexible organizational structures to adapt to rapid growth, with new executive roles emerging, such as Chief Customer Officer and Chief Revenue Officer.
- Key elements of a SaaS org structure need to include job design, departmental coordination, delegation, span of control, and chain of command, which need to align with business strategies.
- The organizational structure evolves with company size and revenue, transitioning from informal roles in startups to more defined hierarchies in larger firms.
- Many SaaS companies are moving towards non-traditional structures that emphasize cross-functional collaboration to enhance customer outcomes.
- Functionly offers tools for creating and optimizing SaaS organizational structures, allowing for adaptability and strategic alignment in rapidly changing environments.
The emergence of cloud computing and fast broadband connections has transformed software delivery over the past decade.
Allied to this trend, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) companies have disrupted industries such as TV (Netflix), music (Spotify) and accounting (Quickbooks) conditioning consumers towards subscription-based licensing.
These evolving business models have also brought on changes in business processes and organizational structures, and industry org charts have evolved to represent the way SaaS companies now operate.
Business-to-business (B2B) SaaS companies are renowned for their hyper-growth success driven by agile product development, experimental customer acquisition, and ongoing customer lifecycle management. Companies such as Docusign, Atlassian and Canva have forced former CD software selling companies such as Microsoft to move to SaaS.
SaaS companies have brought forth new executive roles such as the Chief Customer Officer, Chief Marketing Officer, and Chief Revenue Officer. We will discuss how these fit within a SaaS company org chart and what the typical roles and responsibilities are.
What Is a SaaS Company Org Structure?
An org structure defines how a company's operations are directed to achieve company goals. It outlines how work flows through an organization, along with the various lines of reporting and how groups work together to manage tasks.
Traditional org structures tend to be formalized with employees grouped by function, region, or product line. In startups and less traditional structures, SaaS operations team structure is often more loosely defined and flexible to respond rapidly to evolving needs.
Regardless of the actual org structure that is put in place, the key is to align the structure with the business strategy in four areas:
- Leadership: Who is responsible for developing strategy and monitoring its effectiveness?
- Organization: What structures, processes, and operations will be used to execute the strategy?
- Jobs: What roles and responsibilities are needed for effective operations?
- People: What experience, skills, and competencies are required for the successful execution of the strategy?
When individuals in an organization understand the interdependencies of these four areas as they apply to your business, it facilitates a smoother workflow while allowing for the ability to adapt to changing conditions when necessary.
When thinking about your SaaS operations team structure, there are also five key elements that define the structure:
- Job design: Defining job responsibilities
- Departments: How jobs are coordinated
- Delegation: Which functions or tasks are assigned to positions
- Span of control: Number of employees reporting to managers
- Chain of command: The lines of authority within an organization
Your SaaS roles and responsibilities will also vary based on your management style.
In a centralized model, the authority to make decisions is restricted to those at the highest levels of management with declining authority for subordinates. Think of this as the pyramid approach with those at the top setting policies and strategies for each group below them.
A decentralized style creates a flatter and leaner organization. Lower levels of the org hierarchy have greater decision-making authority and structure may evolve for different tasks or goals.
 Related interactive template: Early Stage SaaS Technical Team Evolution
Related interactive template: Early Stage SaaS Technical Team Evolution
What’s the Best Organizational Structure for Your SaaS Company?
Specifically defining a B2B SaaS org chart can be difficult because each company is unique and has its way of conducting business.
It also depends on the size and scale of your company and where you are in your growth cycle. As you scale, you will need to adapt your SaaS company organizational structure to accommodate your growth.
In other words, you will want to draft your SaaS company org chart to match the way you want to work right now and as your company evolves. The best way to get started is to look at the typical org structure for SaaS companies of varying sizes and see how they line up with your operational goals.
You can approach this in two ways — by the size of the company or by revenue thresholds.
Typical SaaS Organizational Structure – Defined by Size
1 to 5 Employees
As most SaaS companies start with a founder and maybe a few employees, the distribution of labor is typically unstructured. Everybody in the organization is wearing multiple hats and doing whatever it takes to move the company forward.
While there may be a division of tasks, any organization structure must be loosely defined to allow for the flexibility to adapt rapidly as operational priorities evolve.
5 to 10 Employees
In small SaaS companies with five to 10 employees, the founder is typically the highest executive and is responsible for setting the tone and vision. They are also usually responsible for the sales and marketing functions of the company.
Any co-founders will make up the rest of the executive team. If there are no co-founders, the typical SaaS organizational structure will include two high-level managers. One generally manages the product and technology for delivery while the other handles administration, sales, operations, and processes.
Any other employees will report to the management team and may be assigned by areas or jobs.
Small, Flat SaaS Organization Structure (Example)
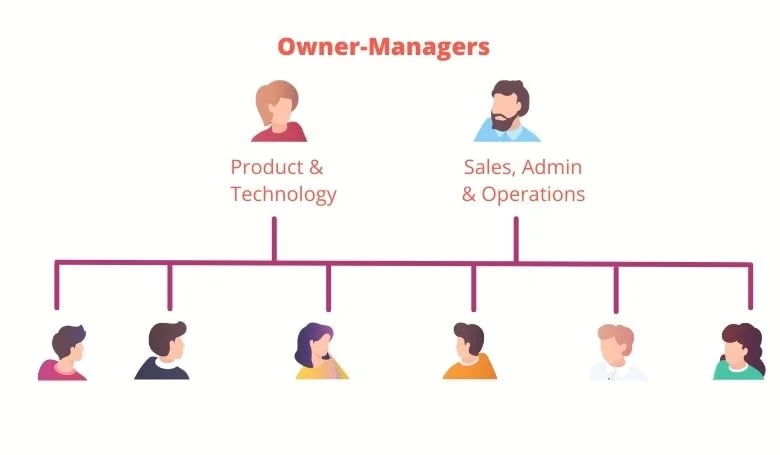 25-50 Employees
25-50 Employees
As the SaaS organization grows, a more formal structure starts to evolve. While the executive team may remain the same, typically more employees are added in key function groups, such as:
- Sales and marketing
- Admin and process
- Product and technology
As employees are brought on board, they will now have assigned roles and responsibilities. Underneath the executive team, the typical org structure for SaaS companies will include a Sales Manager, Product Development Manager, and Marketing Manager.
Org charts tend to follow the more traditional hierarchy of executives, departments, managers, and employees with assigned roles and responsibilities.
50-75 Employees
As SaaS companies grow, the administration, financing, and accounting functions will need resourcing. The next logical step is to start to add C-suite execs.
As companies grow beyond 50 employees, this is the time when a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) and Chief Financial Officer (CFO) are typically brought on board to manage the organization’s operations and finances. Many also choose to add a Chief Information Officer (CIO) or a Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) reporting to a Chief Executive Officer (CEO) at this stage.
Founders may take on these C-suite roles, although many SaaS companies look to seasoned management to fuel growth at this stage.
75+ Employees
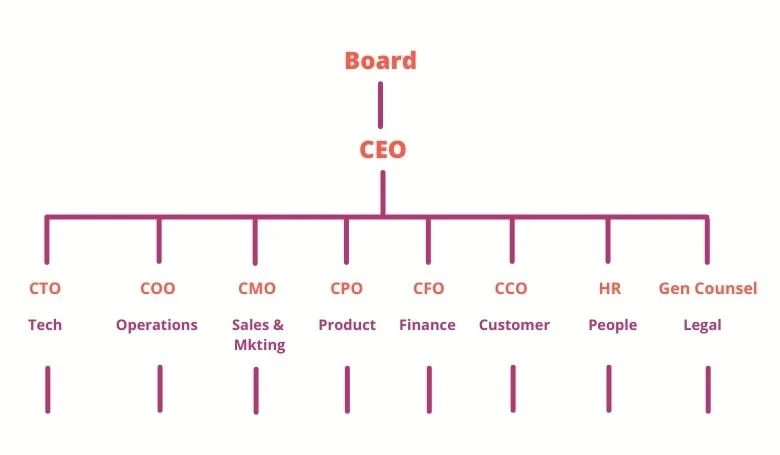
As SaaS companies expand to a larger scale, an even more formal structure may be necessary to operate efficiently. C-suite execs will be on board to guide the operations with Vice Presidents heading defined departments such as:
- Sales
- Marketing
- Finance
- Accounting
- Product Development
- Customer Support
- Human Resources
Within each functional area, there are also likely to be managers or leads that oversee functional groups.
SaaS Organizational Structure – Defined by Revenue
Venture capital firm Redpoint Ventures works with early and growth-stage companies. They surveyed SaaS companies to find how teams grow as startups scale. The 2020 Redpoint Go to Market study shows how teams are structured by revenue.
The survey breaks out structures based on annual recurring revenue (ARR), a key metric used by SaaS and subscription businesses to forecast predictable and recurring revenue. ARR measures the growth momentum for companies.
ARR up to $1 Million
SaaS companies with annual recurring revenue up to $1 million typically have leads for Sales, Marketing, and Customer Success. Founders may lead efforts in one or multiple areas with other key Leads augmenting founder strengths.
ARR $1 to $5 Million
As companies grow their ARR, they also start to increase their headcount. While marketing and customer success continues to have leads, a VP in Sales is typically leading the sales and growth efforts.
ARR between $1M-$5M, median of 21 employees
- 12 engineers
- 6 in sales
- 4 in marketing
SaaS companies invest in engineering at startup and then scale up their go-to-market (GTM) teams as they roll out the product and grow the customer base.
ARR $5M-$20M
As ARR grows beyond $5 million, SaaS companies generally have VPs heading each of the core operational areas. The ratio of engineers to salespeople starts to get closer to 1:1 rather than 2:1 as sales and support are necessary to continue to fuel growth and support customers.
At this level of ARR, the Redpoint study shows that the average SaaS company sees as much as a 10X growth in sales staffing compared to 5X in engineering teams and 4X in marketing teams.
ARR $20M+
At the $20 million and above level, companies typically add a level above the VP rank for sales. A Chief Revenue Officer (CRO) position is added to oversee growth initiatives in the majority of SaaS companies.
Chief Customer Officer and Chief Marketing Officer positions are also established although this varies greatly by company. According to the study, just 10% of SaaS companies with ARR at $20m or above have a Chief Customer Officer.
By comparison, 35% of SaaS companies with ARR in the $20 to $50 million range have a Chief Marketing Officer (CMO) with the percentage growing to 40% at $50 million and 53% at $100 million.
$20M+ Revenue SaaS Organization Structure (Example)
Evolving SaaS Organizational Structures
While looking at SaaS org structures based on headcount and revenue can give you ideas on how to structure your company, there’s really no right or wrong way to do it. Today, many SaaS companies have moved past separate sales, marketing, engineering, and finance areas headed by a senior executive.
SaaS companies have found this traditional structure makes it easy to report activity and revenue, but it may not address the cross-functional customer and product lifecycle management that is critical to maintaining and growing a subscriber base.
SaaS companies often require execution across functional activities which can tend to blur rigid departmental lines, roles, and responsibilities. This non-traditional workflow is focused more on customer outcomes than traditional lines of reporting.
That’s why many of the newer SaaS companies are restructuring their functional management structure and creating new roles, such as Chief Product Officer, Chief Performance Officer, and Chief People Officer.
Chief Product Officer
The CPO is responsible for product development, management, and marketing. CPOs may also be responsible for Customer Success, especially if efforts are focused more on customer engagement, satisfaction, and retention rather than sales. While some companies elevate a Chief Technical Officer (CTO) or Chief Innovation Officer (CINO) to this role, the majority employ both a CPO to oversee product marketing and management and the CTO/CINO handling product development and implementation.
Chief Performance Officer
The Chief Performance Officer (CPO) employs a holistic view of performance throughout the organization and develops measures to assess outcomes and improve them. CPOs often evolve from CFO or CIO roles.
Chief People Officer
The Chief People Officer role often combines CFO and Human Relations functions into one role in some organizations. In other SaaS companies, the Chief People Officer operates separately from the CFO and is responsible for talent acquisition, diversity, training, retention, and HR practices.
Each of these roles works across traditional department lines. Consulting firm Bain & Company calls this approach "integrated management based on value creation."

'Performance' has become a department in Itself | Photo by nappy / Licensed under Pexels License
 : Creating Your B2B SaaS Org Chart
: Creating Your B2B SaaS Org Chart
Creating your SaaS organizational structure and defining SaaS roles and responsibilities is easy with Functionly.
Functionly uses intelligent org design to help you navigate the future and make it simple to optimize your organization and deploy resources.
You can develop a functional org chart in minutes using drag and drop tools. Intelligent mapping allows you to quickly see functional gaps or overlaps.
Just as your organization grows and evolves, Functionly’s org charts grow and evolve with you to help navigate change and see a clearer future. The powerful Scenario Builder tool lets you imagine a future state and strategically align roles and responsibilities as your organization grows.
Functionly also integrates with many of the tools that SaaS companies are already using, such as ADP, Slack, Quickbooks, Zenefits, JustWorks, Bamboo HR, Rippling, Gusto and others.
Want to learn more about how Functionly can help you design your optimal SaaS company organizational structure? Get a free trial and start today.
Learn about other industry org charts.
~~
Sources
- SHRM.org resources and tools
- What’s the Best Organizational Structure for Your SaaS Company? B2BNN Newsdesk, 22 Aug 2021
- What is the Structure of the Typical SaaS Company as it Scales? Tomasz Tunguz, LinkedIn, 22 June 2020
- 2020 SaaS C-Suite Evolving to Support Product and Customer Lifecycle Management, L. Kelley, C-Suite Best Practices, 13 Feb 2020
- 4 Steps to Elevate Functional Effectiveness & Operational Maturity, A. Mani, Functionly
- Don’t panic! And other sound learnings for fast-growing businesses, Functionly




